Thanks to their nutritional characteristics, tomatoes have many health benefits. Rich in water and fiber, they contain many minerals and vitamins that are essential to ensure the proper functioning of the body. They are an important source of vitamin A[1], which plays an important role in bone growth and the synthesis of eye pigments, and vitamin C[2], which is involved in the metabolism of iron by promoting its absorption as well as in other fundamental physiological processes such as the synthesis of red blood cells and collagen.
Lycopene, the antioxidant
One of the most interested compounds of the tomatoes is lycopene, a carotenoid pigment responsible for its deep-red color when ripe. It has strong antioxidant properties, which makes it two to three times more effective than its carotenoid counterparts. Antioxidants can neutralize free radicals, which are permanently produced by the metabolism. These toxic and highly reactive substances induce oxidative stress that leads to aging and cellular degeneration. The high production of free radicals is associated with various factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, bad diet, etc. An external intake of antioxidants via the diet therefore helps to combat cell degeneration. The consumption of lycopene-rich food has been showed to reduce risk of chronic diseases. Studies have shown that a diet rich in lycopene, in particular through a high consumption of tomatoes and tomato products, prevents the occurrence of several types of cancer as well as atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease.
Tomatoes have many health benefits
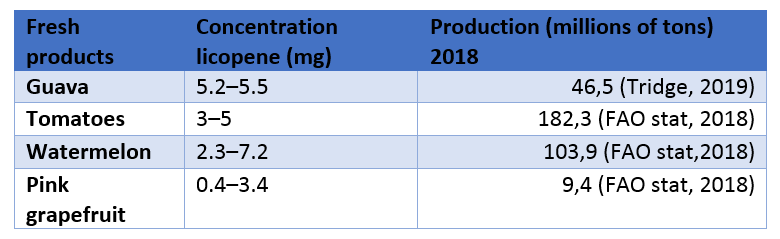
If this pigment can be found in different types of fruits and vegetables (watermelon, red bell pepper, pink grapefruit, etc.), tomatoes are the second most important source of lycopene, after guavas – however they are more easy available than the latter. Produced in large amounts throughout the world, tomatoes remain the most accessible natural source of lycopene.
Futhermore, the lycopene content varies depending on the varieties of tomatoes but also according to production methods. Tomatoes grown in fields and picked mature will have a higher lycopnee content than those in greenhouses and/or picked green. The transformation process also has an important impact on its bioavailability, i.e. the part that is assimilated by the organism. In fact, if this process reduces the lycopene content in the finished product compared to fresh tomatoes, it improves its bioavailability. Because of its lypophilic nature, lycopene absorption is made more efficient if tomato products are consumed with a source of fat.
Read more at: https://www.futura-sciences.com/sante/actualites/medecine-obesite-tabagisme-pourraient-accelerer-vieillissement-humain-6649/; https://www.refiascone.it/?p=1158
[1] 31% of the daily recommended intake for 100g
[2] 31% of the daily recommended intake for 100g